Combing IoT and DLT to Ensure the Safety of the World’s Vaccine Supply Chains
In March 2020, the world was devastated by a global pandemic that fundamentally restructured the way we live and do business. Now, a year to date later, we are lucky to be at the point where multiple vaccines have been approved and administered to the public. Alas, vaccinating the global population against COVID-19 has proved to be one of the biggest challenges humanity has ever faced, both with unique distribution and logistical challenges.
To date, as per March 10th, there have currently been ~93.6 million vaccine doses administered in the US and 23.7 million administered in the UK1.
At the moment, there are multiple different COVID-19 vaccines that have been authorized and recommended, with others in advanced stages of development. While they have all been developed with the same goal in mind, there are substantial differences between the jabs from their composition and reported effectiveness, to their price and ease of conservation, and distribution obligations. For instance, some vaccines are incredibly time and temperature-sensitive, requiring a life of 5-8 days only with temperatures as low as -75C, whereas others can be maintained stable for 30 days at a temperature between 2C and 8C. Needless to say, the logistics and operations of selling, storing, shipping, and administering each of these vaccines is incredibly time-consuming and overwhelmingly manual, only increasing the burden when one administrator must manage large purchase order quantities of two or more different Covid-19 vaccines.
With particular reference to the distribution of the vaccine, a few challenges must be noted. Namely
- Demand Forecasting – What is the total quantity required for shipment
- Supply Chain Management – How it should be sent to purchases and distributed once arrived to host countries
- Quality Assurance – How and by whom it should be administered, and with what specific procedure to ensure appropriate provision
- Monitor and Mitigation – How people who have received the vaccine should be monitored, particularly where potential collateral effects may rise
With these vaccines quickly coming to market, it is no surprise that governments and enterprises around the world are exploring solutions, such as vaccine credentials or digital immunization certificates, that can streamline the rollout of vaccines. Many of these solutions leverage combined emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, Internet of Things, and distributed ledger or blockchain technologies
The Powerful Combination of Internet of Things (IoT) and Distributed Ledger Technologies (DLT)
The combination of IoT and blockchain, in particular, opens the door for new systems that inherently reduce inefficiencies and increase transparency for all involved parties. Take a supply chain for example: the accessibility and geolocation functionality of IoT, paired with the accounting of blockchain and DLTs has created new systems that foster supply chain accountability and integrity unlike any before seen solutions. The coupling of these technologies allow an asset to be tracked from the moment the raw materials are mined and among every step of the supply chain until it is with the end consumer. Without leveraging various device intercommunication capabilities and a strong audit system such as the one perpetuated by DLT, this would be virtually impossible (without large-scale human intervention).
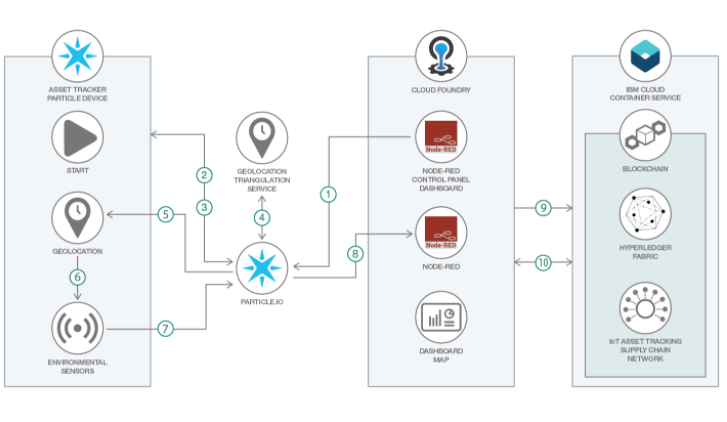

Everis and NTT Data have developed such a tool that combines IoT and Hyperledger Fabric, allowing users to track any type of virtualized asset such as bulk or trade item products, additives, packaging materials, logistic units, and more, from any device. The solution utilizes Hyperledger Fabric to ensure that corresponding transactions are stored and accounted for when reviewing the movement of the assets. This ensures data security, transparency, and an indisputable audit trail, while allowing for automation (via smart contracts), simplification due to a shared truth (ledger), increased security, and certification capabilities.
Future Applications of Blockchain/DLT in Covid-19 Vaccinations
As both Covid-19 vaccines and DLT+ IoT technology solutions remain in their infancy, only early implementations have been seen – as such, we can expect to see a variety of future applications that have not yet been pushed to production. This may include implementations to alleviate key pains including negotiations, logistics, and fraud prevention.
- Supply Chain Integrity and Validity of Origin: Analysts project that Covid-19 vaccines will be the highest demand counterfeit drug on the black market for 20213. Track and trace DLT networks with blockchain-based authenticity certificates could allow purchasers to ensure the origin of the vaccination and track the journey throughout an often global fragmented supply chain. We believe that leveraging IoT and a mature enterprise blockchain such as Hyperledger Fabric would create an accountability and tracking flow to benefit all parties, virtually removing the possibility of receiving fraudulent or counterfeit drugs. In this case, Hyperledger Fabric’s architecture and IoT could benefit the proposed solution as outlined below.
| Hyperledger Fabric(4) | IoT | |
| Flexibility | The programmability of Hyperledger Fabric allows for the flexibility required to digitize complex supply chain operations. For example, trust assumptions for chaincodes are separated from trust assumptions for ordering, ensuring that ordering services can be provided by one set of nodes and tolerate some failure or misbehaviour, depending on the lenience in the business case at hand. It also allows for separate channels per company or shipment, and that endorses may be different for each chaincode, allowing for customization while maintaining privacy and security. In this use case, this is particularly relevant as the system design can be built to ensure end-to-end tracking where any (movement) data is logged or payments are made leaving no room for the entry of malicious actors. | IoT allows for multiple types of devices to communicate with one another achieved thanks to different IoT protocols such as Bluetooth, ZigBee, MQTT or CoAP. This ensures that sensors or equipment, from the time of production through to delivery, can communicate with devices of key stakeholders throughout the entire process, from the time of production through to delivery, adding a layer of reassurance for all parties. There is no room for counterfeit drugs to enter the value chain if tracking is end-to-end. |
| Confidentiality | There is a possibility to add confidentiality requirements to chaincodes, so that content and state of transactions can only be updated if requirements are met. This ensures that the strictest of confidentiality is ensured across the supply chain. | Confidentiality is often embedded in the design of IoT systems. In this use case, it would be key to ensure that the security and authentication measures only permit participants who have defined roles in the system which require the logging of data. As such, end purchasers can review the roles of all parties involved throughout the entire production and shipping process. |
| Consensus | The modular architecture allows for pluggable consensus, which provides an added level of customization. The endorsement policies can include checking the certificate details, roles of the requester, or executing chain code. This allows for originating companies to build a consensus mechanism that suits only their operational process and can remove any possibilities for counterfeit drugs to enter the value chain. It also retains a level of programmability and flexibility, which may be required to build a solution across multi-national vaccine supply chains. | With specific solution design and consented user permissions, there is no room for disruption across IoT devices or networks. |
Cargo Storage Space: With temperature and time-sensitive lifecycles, the vaccines must be shipped in specific conditions. By tracking cargo ship storage space and corresponding vaccinations through asset tracking DLT networks, logistical burdens can be minimized.
Smart Contracts for Negotiations: To date, many governments around the world have found themselves susceptible to private battles with vaccination companies. With high global demand and few verified suppliers, private companies hold essentially all bargaining power. As seen in Canada, Italy, and other countries, this allows the companies to delay sending vaccinations even after payments have been made and force better conditions including import tax payment delays, among other critical legal disputes5. By leveraging a smart contract in the negotiation process, any room for intermediation is removed as they will be self-executing with previously agreed upon terms.
Ultimately, it is clear that there is a strong cause to leverage IoT and DLT technologies to ameliorate the current Covid-19 vaccination system, from logistics to temperature monitoring and negotiations. Though there are currently only a few systems in production, we can assume that the efficiencies brought forth perpetuate more use cases in the future.
- https://www.bloomberg.com/graphics/covid-vaccine-tracker-global-distribution/
- https://developer.ibm.com/patterns/develop-an-iot-asset-tracking-app-using-blockchain/
- https://www.afro.who.int/news/fighting-fake-immunization-travel-certificates-frontier-technologies
- https://hyperledger-fabric.readthedocs.io/en/release-1.3/arch-deep-dive.html
- https://www.ctvnews.ca/health/coronavirus/negotiating-contracts-for-vaccines-in-development-needed-flexibility-anand-1.5218491
Cover image by torstensimon from Pixabay.
Sign up for Hyperledger Horizon & /dev/weekly newsletters
By signing up, you acknowledge that your information is subject to The Linux Foundation's Privacy Policy